Taxpayers can choose whether to litigate tax disputes with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the US Tax Court (Tax Court), federal district court or the Court of Federal Claims. Claims brought in federal district court and the Court of Federal Claims are tax refund litigation: the taxpayer must first pay the tax, file a claim for refund, and file a complaint against the United States if the claim is not allowed. Claims brought in the Tax Court are deficiency cases: the taxpayer can file a petition against the IRS Commissioner after receiving a notice of deficiency and does not need to pay the tax beforehand.
As demonstrated in the chart below, approximately 97 percent of tax claims are instituted in the Tax Court. It should be noted that, after a taxpayer files a petition in Tax Court, the taxpayer no longer has the option of bringing the claim in any other court for the year(s) at issue.
Tax Court Versus Tax Refund Litigation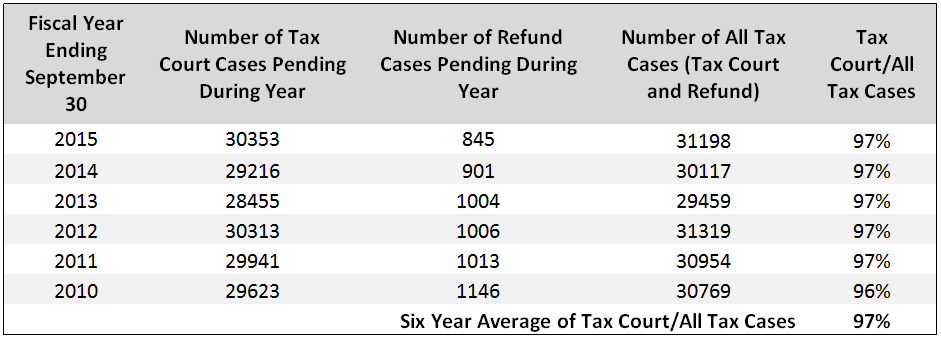
read more

 Subscribe
Subscribe




